
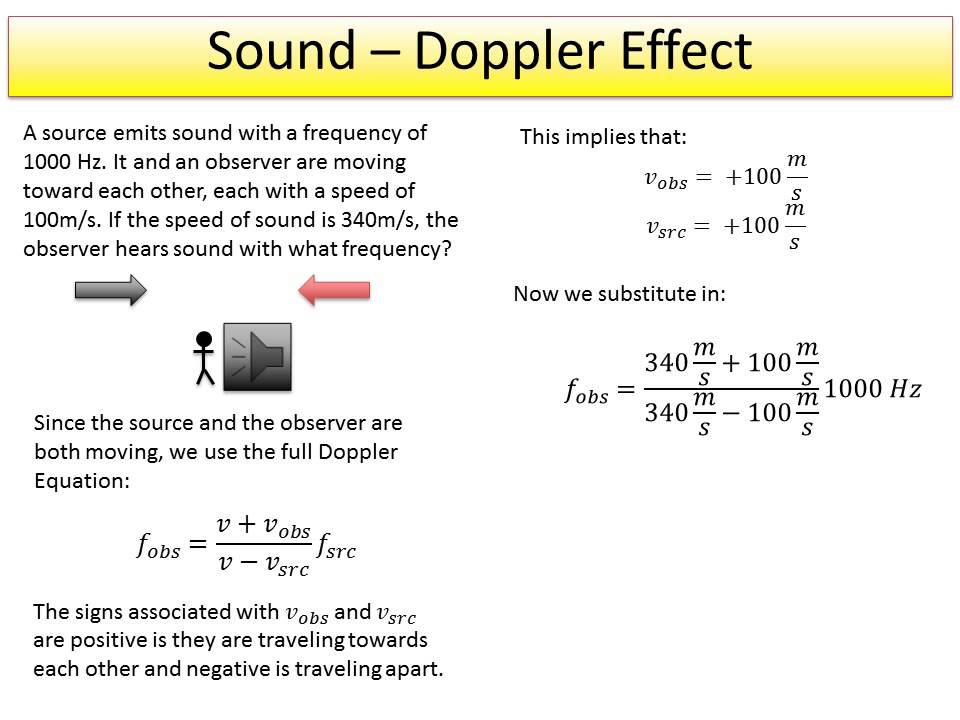

Should she simply aim at the image of the target in the mirror? Explain. They can see their suspect who is around the corner, reflected in a mirror. A police officer has a new sound gun that stuns the criminal.Do sound waves obey the law of reflection? Explain.Give a definition of the law of reflection.If an astronomer notices that the spectrum of colors coming from a star are all shifted towards the red end of the spectrum (the frequencies are lower than they should be) what can she conclude about the motion of the star relative to the earth? (This is one of the pieces of evidence that the universe is expanding nearly all the stars and galaxies around us are moving away from us.).(Hint: Try plugging in some numbers for a car speed in the equation for the Doppler shift for light). (Note: We are talking about the change in pitch, not the change in volume.) But if a car goes past with its lights on we do not notice the Doppler shift for light (the color does not seem to shift towards the red frequencies). If a car goes past with its radio blaring we easily hear the Doppler shift for sound as the car passes (the sound appears to shift from a pitch which is too high to one which is too low).(Police radar and thunderstorm tracking both use the Doppler Effect.) Explain how you could determine the speed of a car or thunderstorm by bouncing radio or microwaves off of them. If the speed of the wave is known and the original and received frequencies are know the speed of the source or observer can be found.\) where \(v\) is the relative speed between the observer and source (positive if they are approaching and negative if they are moving away from each other) and \(c\) is the speed of light. Named after Austrian physicist, Christian Andreas Doppler (1803-1853).


frequency of received sound waves spectral envelope (in continuous and pulsed wave Doppler) above the baseline.source reflecting sound waves is moving toward the emitting source.frequency of received sound waves > frequency of emitted sound waves.an ultrasound transducer) the frequency of the sound waves received will be higher (positive Doppler shift) or lower (negative Doppler shift) than the frequency at which they were emitted, respectively. However, if the reflecting source is in motion either toward or away from the emitting source (e.g. When sound of a given frequency is discharged and subsequently reflected from a source that is not in motion, the frequency of the returning sound waves will equal the frequency at which they were emitted. Doppler shift or Doppler effect is defined as the change in frequency of sound wave due to a reflector moving towards or away from an object, which in the case of ultrasound is the transducer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
